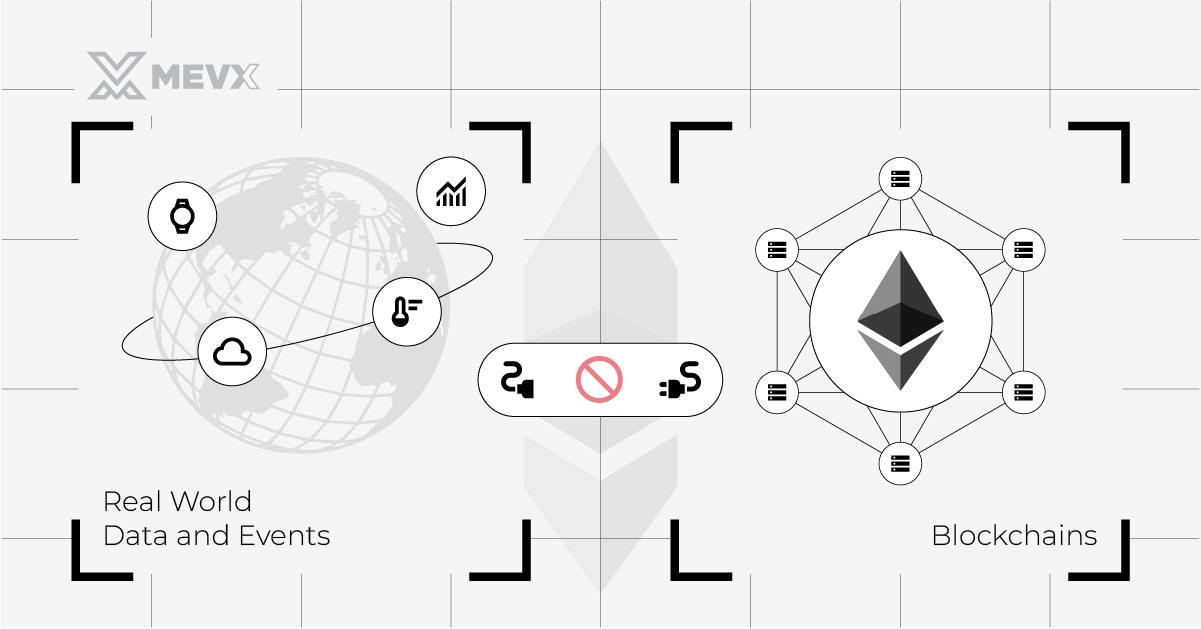
Blockchain technology, particularly Ethereum, has completely changed the world from the moment it was introduced. However, there was a critical issue that prevented the further applications of this technology. Despite its versatility, Ethereum’s capabilities depend on the on-chain data.

With such a limitation, smart contracts deployed on Ethereum can not access information from the real world. The data must be uploaded to the network, burdening the process, thus preventing the further applications of the blockchain.
The data problem of Ethereum blockchain
To bridge this gap, blockchain oracles were created as an efficient solution. These oracles act as a conduit between Ethereum and the external environment.
What Are Ethereum Oracles?
Ethereum oracles, or blockchain oracles in general, are mechanisms that have the sole job of connecting the smart contract with the real world. Automatically, through an oracle, information is obtained from off-chain sources, verified, and delivered on-chain. Finally, thanks to oracles, smart contracts can react to events in the real world.
Not only sending data to the blockchain, Ethereum oracles can also receive data from the blockchain and send it to external systems. This further expands the applicability of Ethereum.
Core Oracle Functions:
- Input: Transferring off-chain data (e.g., weather reports, sports results) onto the blockchain.
- Output: Transferring on-chain data to external systems (e.g., triggering supply chain updates)
- Computation: Performing complex calculations and creating randomness (e.g., lotteries, gacha) off-chain and then sending the results to the network.
By bridging the gap between the blockchain and the external environment, oracles help develop “hybrid smart contracts”. These contracts function based on the codes deployed on-chain and the infrastructure from off-chain.
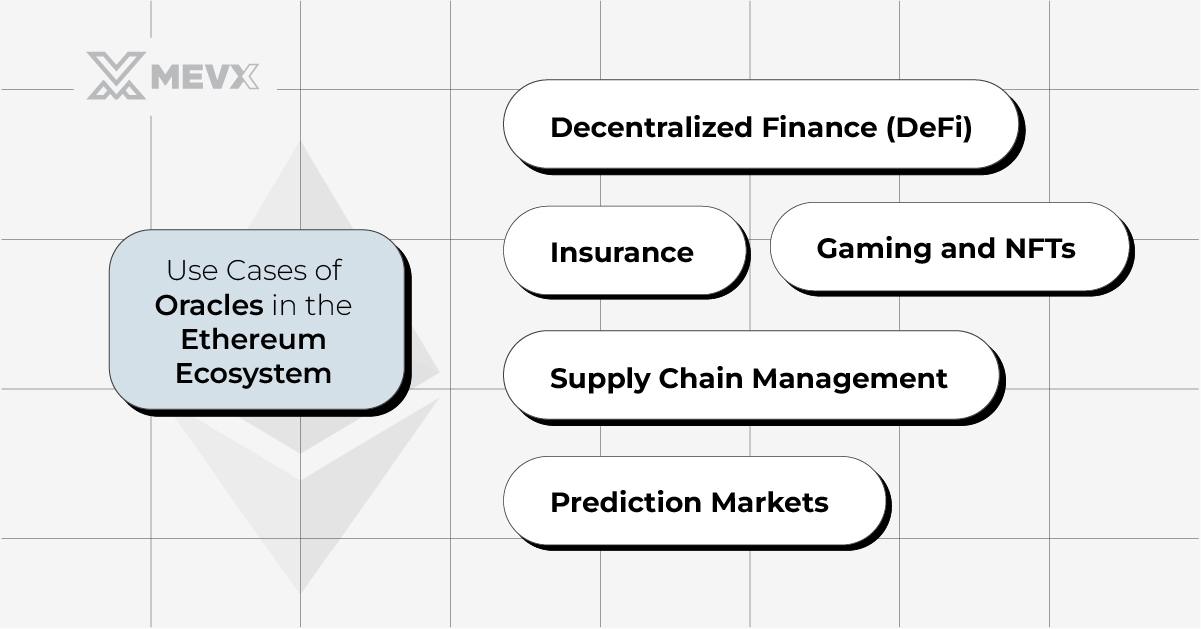
Use Cases of Oracles in the Ethereum Ecosystem
The integration of oracles helps Ethereum support wider use cases. Some of the most prominent ones are:
Use cases of Ethereum oracles
1. Decentralized Finance (DeFi):
Prices of tokens, currencies, and assets are updated in real-time, and oracles direct this information to smart contracts. This makes blockchain possible for use cases like swap, yield, or use as collateral. Moreover, this information is vital for Aave and Compind and many such protocols.
2. Insurance:
Oracles can feed smart contracts with weather data or geospatial data. Based on those smart contracts, automated verification processes can be done with regard to the claims of insurance.
Oracles collect data regarding the temperature and send it back to Ethereum smart contracts, which, in case the temperature goes above, say 40 degrees Celsius, the user can claim insurance.
3. Supply Chain Management:
Oracles receive data like location, temperature, or humidity from devices such as GPS trackers or sensors. Then, the data will be verified and submitted to Ethereum, creating an immutable record of the goods’ journey from origin to destination. This allows all parties in the supply chain to track the movements of goods at every stage, ensuring authenticity and reducing fraud.
4. Prediction Markets:
Prediction markets allow their users to create bets on any event outcomes, including sports, elections, or financial predictions. Once the event has occurred, the oracle draws the confirmed outcome from predefined, reliable sources and broadcasts it to the smart contract of the prediction market. Immediately after the result has been confirmed, the smart contract pays off the participants who have placed correct bets. Events are settled fairly, using oracles, on the outcome determined, a feature employed by platforms such as Augur.
5. Gaming and NFTs:
Oracles create random numbers off-chain and provide them to blockchain apps in a secure and tamper-proof manner. This makes any outcome that relies on randomness, like the dropping of loot, or the traits of NFTs, unpredictable and very fair. Oracles in blockchain-based games guarantee that things such as item drops, the outcomes of battles, or dice rolls are not tampered with by either game developers or participants.
How Decentralized Oracles Mitigate Risks
Decentralized oracles address many issues posed by centralized systems. By distributing the data-fetching process across multiple nodes, they provide stronger guarantees for accuracy and reliability.
Features of Decentralized Oracles:
Consensus Mechanisms: Several oracles source the data independently and validate it, reducing the chance of manipulation.
Economic Incentives: The majority of oracles require staking tokens, where dishonest behavior may be penalized, hence aligning incentives with those who report correctly.
Proof-Based Systems: Chainlink oracles use sophisticated cryptographic proofs together with trusted execution environments (TEEs) to ensure that the data is authentic.
Data Aggregation: The data from different sources gets aggregated into one single input of trust, ensuring resilience to erroneous or malicious sources.
Prominent decentralized oracle solutions, such as Chainlink, UMA, and Witnet, leverage these principles to enhance the security and trustworthiness of blockchain-integrated data.
The Future of Oracles in Ethereum
The future of oracles will evolve with novel blockchain technologies. Further possible development could be executed by the following:
- Cross-Chain Oracles: Interoperability of data between different blockchain chains.
- AI-Integrated Oracles: Machine learning for improved data validation processes.
- Real-Time Data Oracles: Reduces latency, hence upscales high-frequency applications’ performance.
Further improvements will make Ethereum even more useful to innovators for building more decentralized systems and even go deeper into solving the problems of oracles.
Oracles are extremely important for the blockchain ecosystem because they bridge Ethereum to real-world data. More evolution and more adoption are surely going to develop Ethereum’s potential further, creating a new generation of decentralized applications.
Share on Social Media:
