Main Takeaways
- This article discusses what gas fees on the BNB Chain are.
- Reasons why gas fees are important to the BNB Chain are mentioned.
- A simple guide to managing the gas fees is also provided.

Gas fees on the BNB Chain
Introduction
Gas fees are an indispensable element of a blockchain. They come in various forms but are mostly the native token of that network, which is BNB in the case of the BNB Chain.
For users interacting with the BNB ecosystem, whether by staking, transferring, or engaging in dApps, understanding how gas fees work is necessary. This article will cover how BNB gas fees function, explain the importance of gas fees to the BNB Chain, and how to manage gas fees.
What Are Gas Fees on the BNB Chain?
Gas fees, or transaction fees, are small amounts of the native token used to pay for conducting transactions over the blockchain. Specifically, for the BNB Chain, the native cryptocurrency for its ecosystem is BNB. We have an article “The Native Token of BNB Chain” covering the information about BNB.
These fees are a monetary incentive for validators, which are usually entities confirming a set of transactions and adding them to the blockchain. Without these fees, the network would lack an economic way to ensure security and performance.
Every time a transaction is performed, like staking your crypto, sending money to an exchange, or sending some tokens to your friend, it gets automatically cut from the BNB balance in your wallet. Usually, this amount is very insignificant, lying in the range of $0.04 to $0.20 per transaction. These fees are variable, depending on the congestion in the network.
Why Are Gas Fees Important?
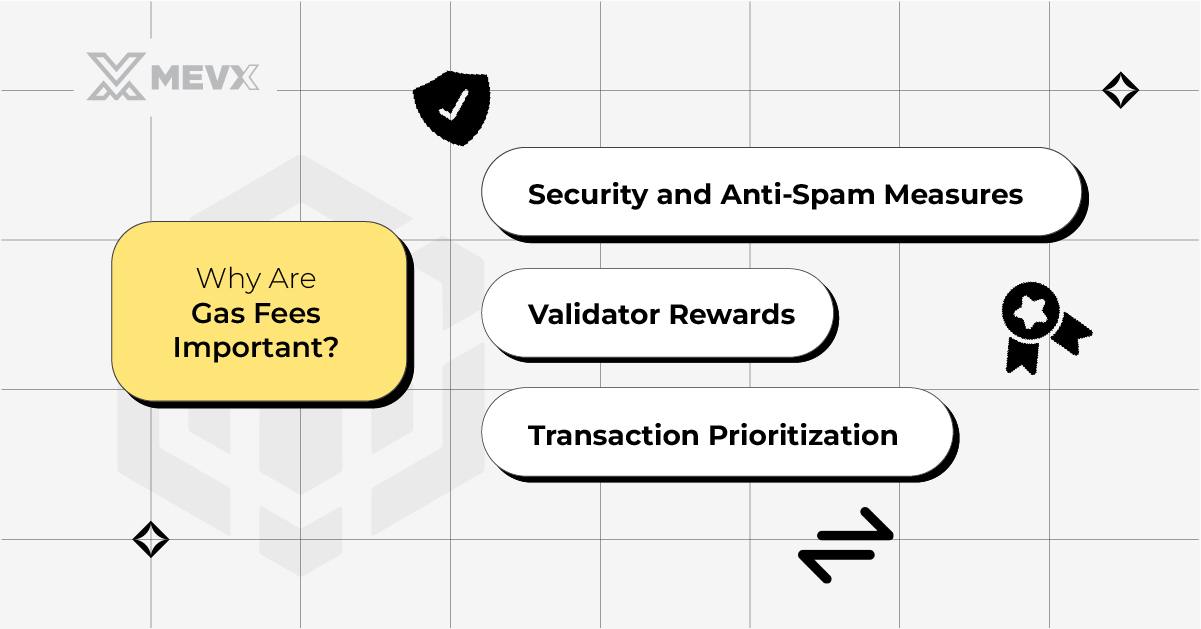
Gas fees are important to the BNB Chain
Gas fees play several pivotal roles within the BNB Chain:
- Security and Anti-Spam Measures: By imposing a cost on every transaction, gas fees deter spam and malicious activity on the network.
- Validator Rewards: The BNB Chain rewards validators with a portion of gas fees, ensuring their continued participation and maintenance of the blockchain.
- Transaction Prioritization: Users can pay higher gas fees to prioritize their transactions during times of high network activity.
However, it’s important to note that users must have a small balance of BNB in their wallet before initiating any transaction on the BNB Chain. Without sufficient BNB, transactions cannot be executed, including staking or transferring other cryptocurrencies.
How to Manage Gas Fees Effectively
A common mistake of new users is not having enough BNB in their wallet to cover transaction fees. For new users or those not used to the BNB Chain, this is how you can ensure smooth operations:
- Create A BNB Wallet: You need to have a wallet suitable for the BNB Chain. You can follow our guide on How to choose a BNB wallet and How to set up a BNB wallet to create one.
- Fund Your Wallet: Buy some BNB from exchanges like Binance, then send part of it to your wallet. Leave some in an account to provide for the balance for further transaction fees.
- Understand Bridged Assets: If your wallet holds bridged assets like Ethereum on the BNB Chain but lacks BNB, you’ll need to acquire some BNB first to enable transactions involving those assets.
- Monitor Network Conditions: The gas fees will change depending on network conditions. During congestion, the fees might temporarily rise. Therefore, plan your transactions accordingly.
If the BNB amount in your wallet is insufficient to perform a transaction, you will need to buy it from an exchange and send it to your wallet. This can cause some unnecessary expenses. Therefore, always remember to have BNB available in your wallet.
Conclusion
Gas fees on the BNB Chain are necessary for the proper functions of the network. This article has covered various points related to the gas fees on the BNB Chain, from what the BNB gas fees are, their importance, and how to manage your gas fees.
Share on Social Media:
