Ethereum is more than just a blockchain; it’s a decentralized revolution that empowers users to take control of their financial sovereignty. But to fully embrace the Ethereum ethos, you need to do more than just hold ETH, you need to run your own Ethereum node.

What Does It Mean to Run an Ethereum Node?
Running a node means operating software, known as a client, that downloads and verifies every Ethereum block and transaction. This ensures the integrity of the network and keeps you updated with real-time blockchain data.
- Software: A client syncs with the blockchain, validates transactions, and helps other nodes stay up to date.
- Hardware: While a personal computer can run a node, dedicated hardware ensures efficiency and uptime.
- Online Presence: A node remains operational as long as it’s online, resyncing when reconnected if it goes offline.
See also Ethereum: The ‘World Computer’ Transforming Blockchain and Finance
Who Should Run an Ethereum Node?
Contrary to common belief, you don’t need to stake ETH to run a node. Nodes hold validators accountable and serve an essential role in Ethereum’s decentralization. While running a node doesn’t generate direct financial rewards like staking does, it provides significant benefits:
- Privacy: Eliminate reliance on third-party servers.
- Security: Verify transactions independently.
- Censorship Resistance: Avoid restrictions imposed by centralized nodes.
- Network Health: Strengthen Ethereum’s decentralization.
- Control: Ensure you dictate the rules you follow in the event of a chain fork.
Why Run a Node? Key Benefits
- Privacy & Security
When you rely on public nodes, your transaction data, including IP addresses and wallet information, can be exposed. Running your own node allows you to interact securely and independently with the Ethereum network. - Censorship Resistance
Third-party nodes can censor transactions from specific IP addresses or accounts. Running your own node ensures you can broadcast transactions whenever necessary without interference. - Participation in the Ethereum Revolution
Every additional node contributes to Ethereum’s decentralization, preventing power from becoming concentrated in centralized servers. - Strengthening Decentralization
More independent nodes mean a more resilient network, reducing vulnerabilities from centralized cloud services that could be targeted by regulators or attackers. - Control in the Event of a Fork
A fork can split Ethereum into two chains with different rules. Running your own node ensures you retain the power to decide which version to support. - Sovereignty
Owning an Ethereum wallet grants control over your assets, but it still depends on third-party nodes for transaction validation. Running your own node is the next step toward full blockchain sovereignty.
How to Run an Ethereum Node
The following are how you can run an Ethereum Node:
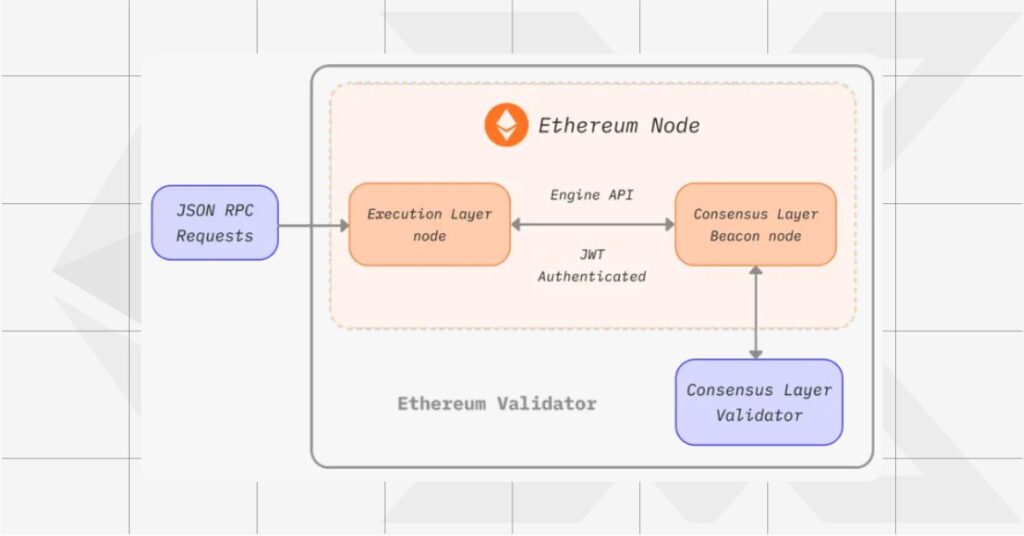
1. Choose Your Ethereum Client
Different Ethereum clients serve different needs. The most popular options include:
- Geth (Go Ethereum): Robust and widely used.
- OpenEthereum (formerly Parity): Optimized for performance and memory efficiency.
- Besu (Hyperledger Besu): Ideal for enterprise use.
- Nethermind: .NET-based client with strong performance.
2. System Requirements
To run a full node, your system should have:
- Storage: 2-4 TB SSD
- RAM: At least 16 GB
- CPU: Modern Intel i5 or equivalent
- Internet: High-speed with no data cap (syncing involves downloading hundreds of GBs)
3. Installation Process
- Download the chosen client from the official website.
- Install and configure it according to your requirements.
- Sync the blockchain using the –syncmode “fast” option in Geth for quicker setup.
4. Configuration & Security
- Set up automatic startup with a service manager (like systemd on Linux).
- Secure your node with firewalls and regular updates.
- Monitor logs and manage storage as the blockchain grows.
Why It Matters
Running an Ethereum node isn’t just a technical endeavor, it’s a commitment to decentralization, privacy, and security. It enhances:
- Network Integrity: Nodes verify and propagate transactions, keeping Ethereum trustless.
- Data Privacy: Avoid exposing transaction data to centralized services.
- DApp Performance: Many decentralized applications rely on nodes for fast and reliable execution.
- Governance & Voting: If staking, a personal node allows independent decision-making in protocol updates.
- Education & Development: Gain hands-on experience with blockchain technology.
Final Thoughts
Ethereum thrives on decentralization, and running a node is one of the best ways to contribute. Whether you’re an investor, developer, or blockchain enthusiast, operating a node is a step toward true sovereignty in the crypto space. If you believe in the Ethereum vision, it’s time to take control.
Don’t miss out on any articles and updated trends on Ethereum, follow MevX now!
Share on Social Media:
