Main Takeaways
- This article covers what Ethereum bridges are and how they work.
- We aim to provide the benefits and the importance of Ethereum bridges.
- Some challenges that need to be resolved are mentioned.

Bridges in the Ethereum network
Introduction
Ethereum is the most utilized blockchain platform, featuring high-throughput smart contracts and a rich ecosystem of decentralized applications. This high-traffic network is suffering from scalability challenges that hamper the interoperability of Ethereum with other blockchain networks. This is where the bridges of Ethereum have come in, imposing one pivotal solution on such challenges, thereby offering unrestricted flows of assets and data between Ethereum and other blockchain systems.
In this article, we show what Ethereum bridges are, how they work, their advantages, and why they are a must within the evolving blockchain world.
What Are Ethereum Bridges?
Ethereum bridges usually refer to specific protocols designed to connect Ethereum with other blockchains. It helps in transferring not only digital assets but also data, along with functionality over the bridges. This thereby bridges the ecosystems, allowing users to access a wider range of decentralized applications and services without being confined to one blockchain.
There are two main types of Ethereum bridges:
- Trustless Bridges: These use smart contracts to automate and secure asset transfers without requiring intermediaries. They align closely with the decentralized ethos of blockchain technology.
- Centralized Bridges: These depend on intermediaries or trusted third-party validators to facilitate and validate cross-chain transactions. They usually provide faster but less decentralized solutions.
Both types of bridges are essential and fill scalability and interoperability gaps within the Ethereum network. Also, they allow users to efficiently interact with a good deal of blockchain ecosystems.
How Do Ethereum Bridges Work?
Technically, the bridges over Ethereum work by locking the assets on the source blockchain and then minting the equivalent tokens on the destination blockchain. Here’s a simplified breakdown of the process:
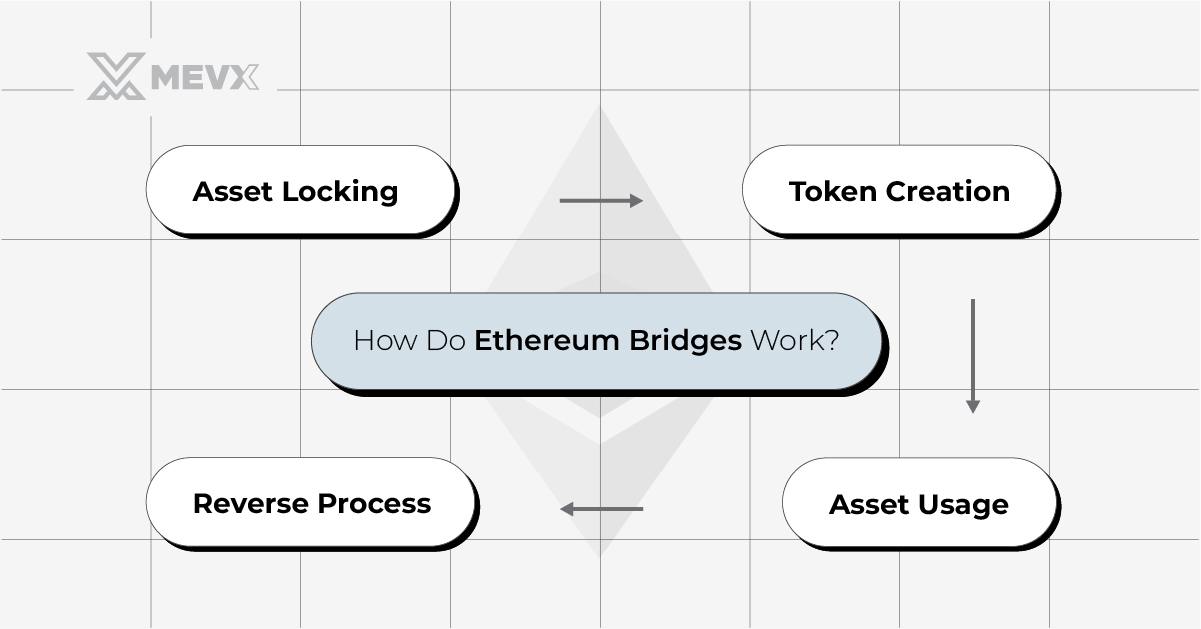
How Ethereum bridges work
- Asset Locking: This involves the user first relocating the assets to some smart contract on the source blockchain and, after that, being able to get locked onto an address for security reasons.
- Token Creation: The bridge protocol will create the targeted blockchain tokens of value at the same level as those being locked.
- Asset Usage: The freshly minted tokens should be freely used either for transactions or within DApps on the targeted chain.
- Reverse Process: Later, equivalent value tokens are burnt on the destination blockchain so that the locked asset on the source blockchain can be unlocked.
This would further fix how cross-chain assets are moved across blockchains.
Benefits of Ethereum Bridges
- Interoperability: Bridges open up the Ethereum DApps and services for usage on other blockchains, increasing utility within the ecosystem.
- Scalability: This relieves congestion on Ethereum by offloading transactions onto other blockchains, hence reducing gas fees.
- Enhanced Liquidity: Bridges make the flow of assets between networks smooth, hence increasing market liquidity and enabling diversified investments.
- Developer Innovation: Bridges open the possibility of building highly advanced applications between chains, creating innovation within the blockchain ecosystem.
Examples of Prominent Ethereum Bridges
Several Ethereum bridges feature a special combination of functionality and usability:
- Polygon Bridge: A Layer-2 scaling solution that provides fast and cheap transfers of Ethereum and tokens between Ethereum and the Polygon network for high-throughput DApps.
- Arbitrum Bridge: A trustless bridge that aims to increase transaction throughput without sacrificing security, courtesy of optimistic roll-ups.
- Avalanche Bridge: A bridge connecting Ethereum and Avalanche to allow cheap and fast transfers.
- Wormhole: This allows asset transfers between Ethereum and other blockchains like Solana. It supports most token standards, including NFTs.
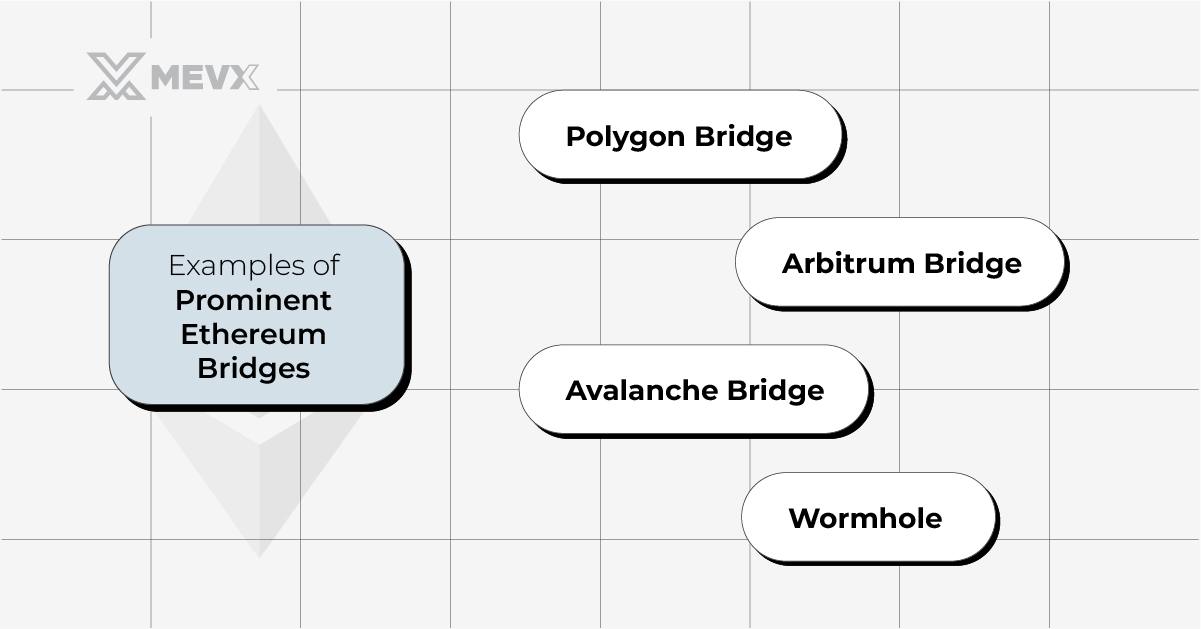
Examples of Ethereum bridges
Challenges and Risks of Ethereum Bridges
Ethereum bridges have their benefits, but they also come with specific risks:
- Smart Contract Vulnerabilities: Exploits to bridge contracts lead to loss of assets.
- Centralization Risks: Centralized bridges can lead to single points of failure and censorship.
- Cross-Chain Attacks: A bug in one network could provide a loophole that compromises different assets on connected blockchains.
This can be mitigated by the use of reputable bridges and following best practices to secure user assets.
Why Do Ethereum Bridges Matter?
Ethereum bridges foster interoperability within this blockchain space. This satisfies the need for increased interaction and access to more applications while relieving Ethereum of scaling challenges. This creates a bedrock for the future where blockchains work harmoniously, encouraging creativity and use cases within the decentralized world.
In conclusion, Ethereum bridges are not just a technical solution but a catalyst to a more connected and scalable blockchain world. The bridges will only gain more relevance as the technology of blockchain progresses. They will take their rightful place as one of the most important tools in a decentralized ecosystem.
Share on Social Media:
